Paragon Active Assurance & TWAMP
By Aravind
Juniper routers have protocols to monitor performance using RPM (Real time performance monitoring) . It utilizes active probes to monitor network performance. Service interfaces (Si-) are used where inline monitoring is enabled. RPM has multiple probe types such as ICMP, TCP, UDP. Some are supported on RE based mechanism and not entirely inline. (ex: BGP, HTTP)
What is Jitter ? it is the difference in relative transit time between two conssecutive probes.
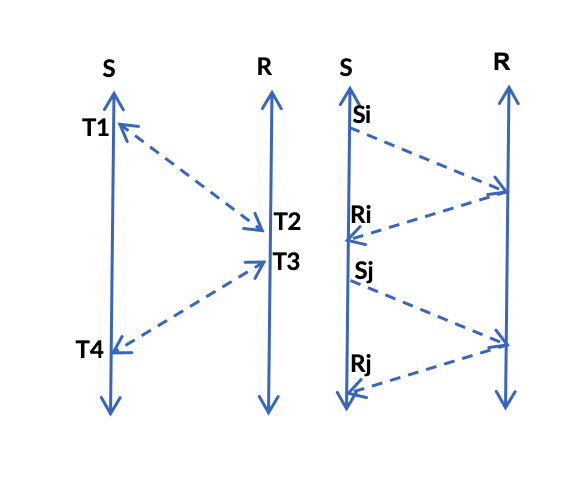
D(i,j) = (Rj - Sj) - (Ri - Si) where S is the probe sender ,R is the probe responder and D(i,j) is the measure of jitter between probes i and j in the direction source to destination. The probe responder simply turns the packet around.
- Round Trip Time (RTT): (T4 - T1) - (T3-T2)
- Egress delay : (T2 - T1)
- Ingress delay: (T4 - T3)
For RE based time stamp, the value is inserted by the kernel and for the hardware based timestamp, they are taken from the packet which was filled by the PFE ukern.
TWAMP (Two Way Active Measurement Protocol)
Open protocol for measuring two way metrics. This is written as part of RFC 5357
+------------------+ +---------------------+
| | control | server |
| control-client +----------------------+ |
| | | |
| session-sender +----------------------+ session reflector |
| | test | |
+------------------+ +---------------------+
The control and session need not be on the same system.
- TWAMP-Control : Used to initiate, start and stop test sessions
- TWAMP-Test: Used to exchange test packets between session sender and session reflector
Session sender and session reflector exchange test packets according to the TWAMP-test protocol for each active session. The control client initiates requests for TWAMP test sessions. The TCP connection gets initiated on port 862 using TWAMP control protocol. Session stop comes only from control client. DSCP values can be set in the TCP SYN packets as well as part of various tests.
In case of need to run TWAMP reflector/server from within a VRF, a mapping needs to happen and needs to run on a port other than 862.
Configuring TWAMP reflector
[edit interfaces]
+ si-0/0/0 {
+ unit 0 {
+ family inet;
+ }
+ unit 10 {
+ rpm twamp-server;
+ family inet {
+ address 31.168.222.11/32;
+ }
+ }
+ }
root@R8# show | compare rollback 1
[edit chassis]
+ fpc 0 {
+ pic 0 {
+ inline-services {
+ bandwidth 1g;
+ }
+ }
+ }
[edit]
+ services {
+ rpm {
+ twamp {
+ server {
+ authentication-mode none;
+ port 862;
+ client-list Client1 {
+ address {
+ 30.1.1.2/32;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
Here the address 30.1.1.2 are the test agents/client which would send the test packets. If a client list is configured only those addresses are allowed to talk to the TWAMP server. Rest would be rejected to make a connection to the port 862 (default). If the si- interface would be placed in a VRF, then the below config needs to enabled. Notice that the ports used are different than 862
root@PE1> show configuration services
rpm {
twamp {
server {
routing-instance-list {
VRF1 {
port 900;
}
VRF2 {
port 901;
}
VRF3 {
port 902;
}
}
Here TWAMP server listens on port 900 for VRF1, 901 for VRF2 and 902 for VRF3.
Couple things to ensure
- enhanced-ip should be enabled under [ edit chassis fpc ]
- Although multiple units can be configured under si- interfaces only one unit can run the knob
rpm twamp-serverto act as a twamp server This would mean you can have only one TWAMP server/reflector per PIC. - If we need to design where TWAMP reflectors need to be present per VRF , we can use VRF leaking
- Create a common dedicated TWAMP VRF where TWAMP server is reachable and leak routes to other VRFs so that packets are reachable
- Create si interface per PIC and place them individually in VRFs. THis is not scalable since there would be limitations based on line cards. If the number of test VRFs are limited this is an option that can be considered since its easier to manage from config perspective.
- Let TWAMP server run on global 862 port and leak routes to the VRFs. Here things act on global table but follows design of option 1 closely.
The above config is for TWAMP full. In case TWAMP lite needs to used,
set services rpm twamp client control-connection c1 control-type light # Client side
set services rpm twamp server light port <port-number> # Server side
TWAMP light
- Helps in larger scale deployments of servers
- removes control plane TCP session. So responder performance is improved and allows to rapidly respond.
- Stateless version of TWAMP full where test params are predefined instead of negotiated.
Scale
TWAMP full
- 500 sessions
- 2 sockets needed (1 for control and 1 for sending probes)
- RE is responsible for managing concurrent sessions where Junos kernel scale comes into play. Around 1k concurrent connections.
TWAMP light
- 1000 concurrent light sessions for server/client
Paragon active assurance
Paragon active assurance helps in generating active L2-L7 traffic generation and helps in testing, monitoring of networks. Can be used as a SaaS or Onprem environments. These data plane metrics help in validating/understanding/resolving underlying quality issues. Consists of 2 parts
- Control center : The control center hosts the GUI. The tests/config will be controlled from here.
- Test agents:
- Available in VM or container form factor
- Can be hosted on on prem/azure/AWS
These tests can be automated using YANG/REST APIs.
Type of tests
Variety of tests are available.
- Stateful TCP, UDP
- IPTV and OTT Video
- Voice
- Internet performance
- Remote packet inspection
- Wifi
Setup
- Follow the instructions at https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/active-assurance3.1/paa-install/topics/concept/introduction.html
- It is a 1-1 follow, do not miss any steps
- If the VM is inside the server with no direct reachability
SSH tunnel to access the port 443
ssh -L 8845:192.168.2.3:443 root@10.85.47.161
Container based test agents
Load image
docker load –i paa-test-agent-application-container_3.1.0.19_amd64.tar.gz
Register the test agent
docker run --rm -v $(pwd):/config paa/test-agent-application:3.1.0.19 \
register --config /config/agent.conf \
--ncc-host 192.168.2.3 \
--account paa \
--api-token ZtbAJuxobha99kiOHCa4LaNmN4P6ZMVpPfe68sgC \
--name paa-agent1 \
--ssl-no-check
- ncc-host: The host ip where control center is running
- account: active assurance account used. Can be retrieved from
ncc user-list - api-token : This can be retrieved under users in GUI. Or as an alternative you can use username and password.
root@paa-server:~# ncc user-list
Users list
xyz@abc.net
Access: active
Accounts:
Name: paa (paragon active assurance)
Permission: admin
Status: owner
confd@netrounds.com
Access: active
Accounts:
Start the container
docker run -d --privileged -v $(pwd):/config paa/test-agent-application:3.1.0.19 --config /config/agent.conf
This will start the container and have it registered on the control center. It must now be visible.
Add secondary interfaces to the container
you can add any number of interfaces to your docker container using veth interfaces. I use the script to achieve the same. The script can be found here
python veth_connect.py -action cveth -name eth1:R88 << create a veth pair
veth with name eth1 and peer-name R88 created
python veth_connect.py -action conn -name eth1 -ip 30.1.1.2/30 -container 643a4bf43dce
entered here
Above command well move one interface into the TA container
brctl addif R8_CE R88 << will move the other end of veth into bridge R8_CE where VM interface is connected
Note: Note: ensure TA is reachable to the TWAMP reflector IP. You will have to add routes within the TA container accordingly if its network is not reachable
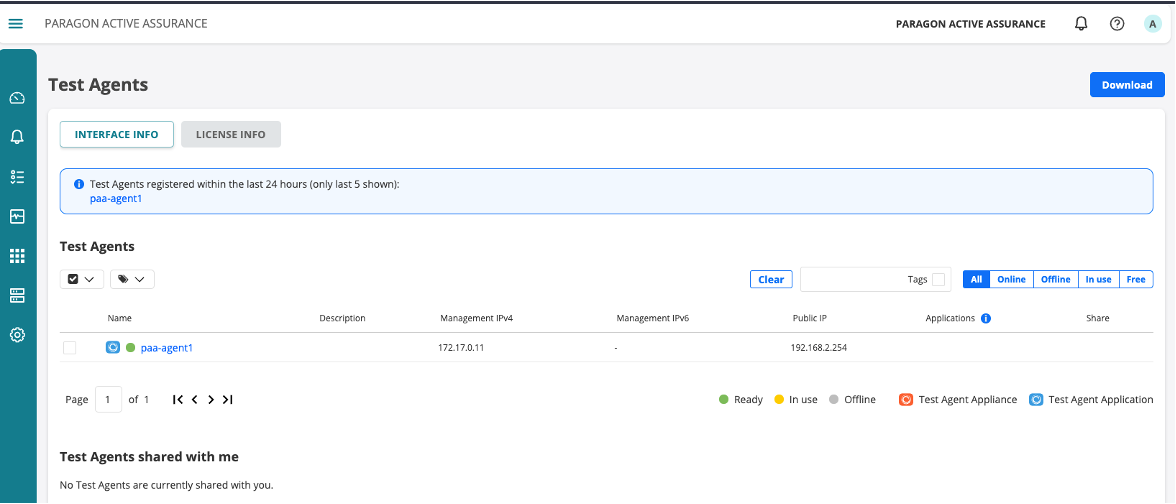
Configure TWAMP reflector in settings in GUI
Go to account and settings –> TWAMP –> Add new reflector

Create a new test
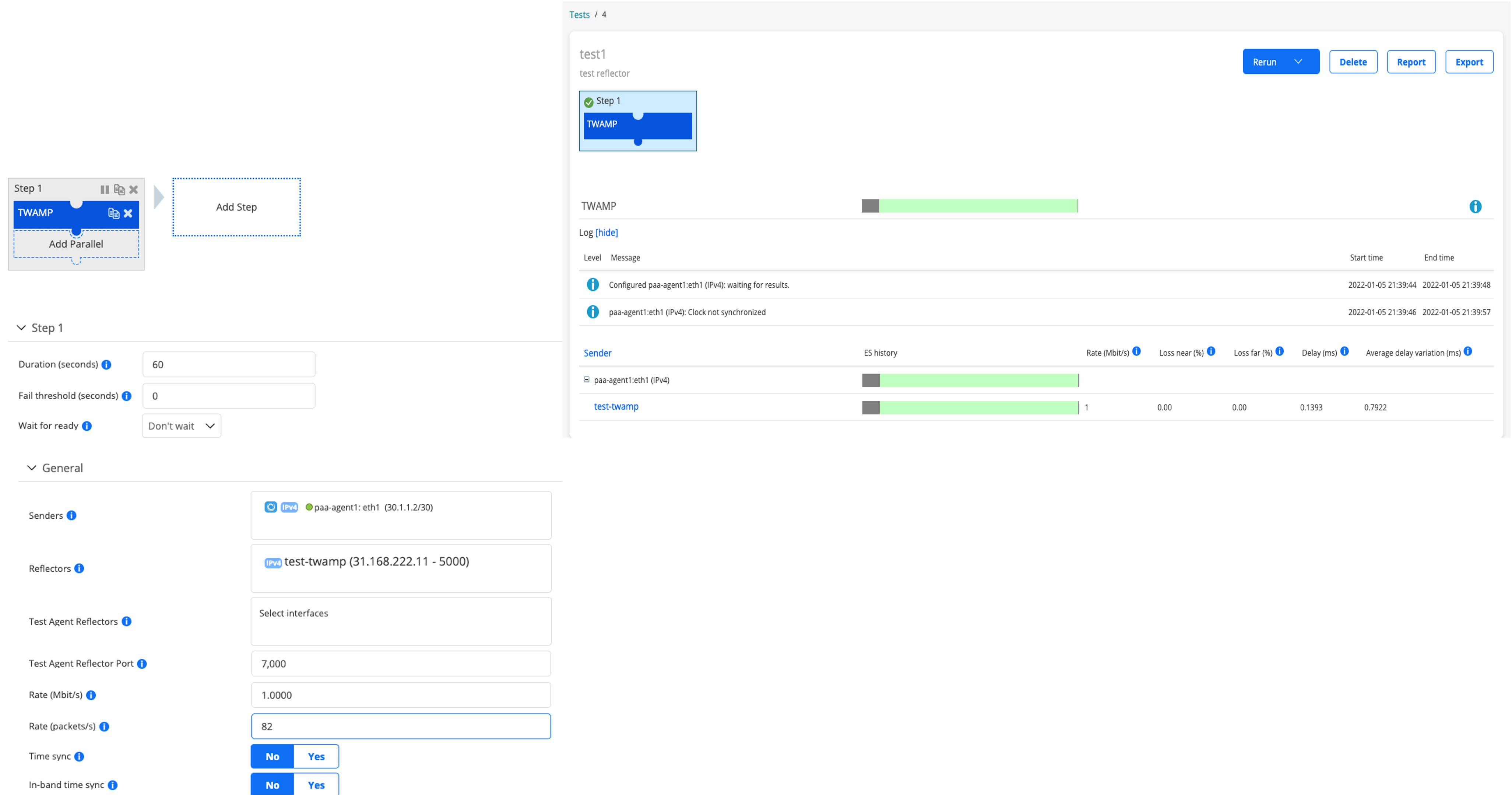
notice the traffic on ingress interface on the vMX
Delay: 2/0/5
Interface: ge-0/0/2, Enabled, Link is Up
Encapsulation: Ethernet, Speed: 1000mbps
Traffic statistics: Current delta
Input bytes: 85203604 (986368 bps) [764888]
Output bytes: 16352792 (986368 bps) [763048]
Input packets: 61798 (89 pps) [638]
Output packets: 13010 (89 pps) [608]
Error statistics:
Input errors: 0 [0]
Input drops: 0 [0]
Input framing errors: 0 [0]
Carrier transitions: 1 [0]
Output errors: 0 [0]
Output drops: 0 [0]
Using multiple Si- interfaces each mapped to VRF
+--------------------+ +----------------------+
| | | |
| +------+ | | +-------+ |
| | paa-1+-+--------------------------------+--+paa-1 | |
| +------+ | | +-------+ |
| | | |
| +------+ | | +-------+ |
| |paa-2 +-+--------------------------------+--+paa-2 | |
| +------+ | | +-------+ |
| | | |
| +------+ | | +-------+ |
| |paa-3 +-+--------------------------------+--+paa-3 | |
| +------+ | | +-------+ |
| | | |
| +-----+ | | +--------+ |
| |paa-4+--+--------------------------------+--+paa-4 | |
| | | | | +--------+ |
| +-----+ | | |
| | | |
| | | |
+--------------------+ +----------------------+
TWAMP server Configs
set chassis fpc 4 pic 0 inline-services bandwidth 1g
set chassis fpc 4 pic 1 inline-services bandwidth 1g
set chassis fpc 4 pic 2 inline-services bandwidth 1g
set chassis fpc 4 pic 3 inline-services bandwidth 1g
=set interfaces si-4/0/0 unit 0 family inet
set interfaces si-4/0/0 unit 10 rpm twamp-server
set interfaces si-4/0/0 unit 10 family inet address 11.2.1.1/32
set interfaces si-4/1/0 unit 0 family inet
set interfaces si-4/1/0 unit 10 rpm twamp-server
set interfaces si-4/1/0 unit 10 family inet address 11.1.1.1/32
set interfaces si-4/2/0 unit 0 family inet
set interfaces si-4/2/0 unit 10 rpm twamp-server
set interfaces si-4/2/0 unit 10 family inet address 11.3.1.1/32
set interfaces si-4/3/0 unit 0 family inet
set interfaces si-4/3/0 unit 10 rpm twamp-server
set interfaces si-4/3/0 unit 10 family inet address 11.4.1.1/32
set routing-instances PAA-1 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances PAA-1 interface si-4/0/0.10
set routing-instances PAA-1 interface ae0.10
set routing-instances PAA-2 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances PAA-2 interface si-4/1/0.10
set routing-instances PAA-2 interface ae0.20
set routing-instances PAA-3 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances PAA-3 interface si-4/2/0.10
set routing-instances PAA-3 interface ae0.30
set routing-instances PAA-4 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances PAA-4 interface si-4/3/0.10
set routing-instances PAA-4 interface ae0.40
set services rpm twamp server routing-instance-list PAA-1 port 900
set services rpm twamp server routing-instance-list PAA-2 port 901
set services rpm twamp server routing-instance-list PAA-3 port 902
set services rpm twamp server routing-instance-list PAA-4 port 903
set services rpm twamp server authentication-mode none
set services rpm twamp server port 862
set services rpm twamp server client-list WIPM_SERVERS address 12.1.2.50/32
set services rpm twamp server client-list WIPM_SERVERS address 12.2.2.50/32
set services rpm twamp server client-list WIPM_SERVERS address 12.3.2.50/32
set services rpm twamp server client-list WIPM_SERVERS address 12.4.2.50/32
TWAMP Client Configs
set routing-instances PAA-1 routing-options static route 11.2.1.1/32 next-hop 12.1.2.49
set routing-instances PAA-1 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances PAA-1 interface ae10.10
set routing-instances PAA-2 routing-options static route 11.1.1.1/32 next-hop 12.2.2.49
set routing-instances PAA-2 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances PAA-2 interface ae10.20
set routing-instances PAA-3 routing-options static route 11.3.1.1/32 next-hop 12.3.2.49
set routing-instances PAA-3 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances PAA-3 interface ae10.30
set routing-instances PAA-4 routing-options static route 11.4.1.1/32 next-hop 12.4.2.49
set routing-instances PAA-4 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances PAA-4 interface ae10.40
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-1 destination-port 900
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-1 routing-instance PAA-1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-1 target-address 11.2.1.1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-1 test-count 1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-1 test-interval 2
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-1 test-session PAA-11 target-address 11.2.1.1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-1 test-session PAA-11 probe-count 20
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-1 test-session PAA-11 probe-interval 2
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-2 destination-port 901
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-2 routing-instance PAA-2
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-2 target-address 11.1.1.1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-2 test-count 1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-2 test-interval 2
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-2 test-session PAA-22 target-address 11.1.1.1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-2 test-session PAA-22 probe-count 20
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-2 test-session PAA-22 probe-interval 2
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-3 destination-port 902
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-3 routing-instance PAA-3
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-3 target-address 11.3.1.1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-3 test-count 1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-3 test-interval 2
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-3 test-session PAA-33 target-address 11.3.1.1
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-3 test-session PAA-33 probe-count 20
set services rpm twamp client control-connection PAA-3 test-session PAA-33 probe-interval 2
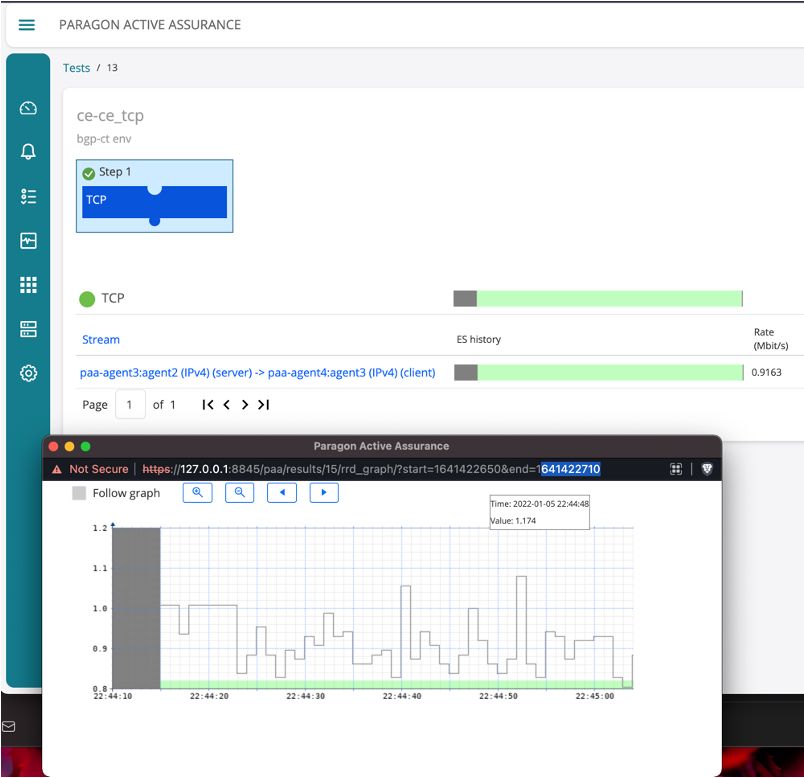
Results
root@clavicle> request services rpm twamp start client PAA-1
root@clavicle> request services rpm twamp start client PAA-2
root@clavicle> request services rpm twamp start client PAA-3
root@D2IPE-II-RE0> show services rpm twamp server
Connection Client Client Server Server Session Auth
ID address port address port count mode
9 12.1.2.50 51214 11.2.1.1 900 1 Unauthenticated
10 12.2.2.50 54091 11.1.1.1 901 1 Unauthenticated
11 12.3.2.50 61419 11.3.1.1 902 1 Unauthenticated
Session Connection Sender Sender Reflector Reflector Session Auth
ID ID address port address port state mode
9 9 12.1.2.50 10008 11.2.1.1 10008 Active Unauthenticated
10 10 12.2.2.50 10009 11.1.1.1 10009 Active Unauthenticated
11 11 12.3.2.50 10010 11.3.1.1 10010 Active Unauthenticated
Using Host PFE based timestamping
Using si-* interfaces, although provides the most accurate timestamping, there are limitations on the inline service interfaces.
Some of them are
- only one TWAMP reflector/server per IFL
- you can enable more than one si- interface by using different PICs. Cards like MPC7E support upto 4 tunnel pics so 4
si-*interfaces can be used. - flexible and scalable to multiple VRFs
- no need for si- interface allowing configs to be simple .
- can you underlying interface of lo0.x interfaces
Configs server side
root@PE1# show services
rpm {
twamp {
server {
routing-instance-list {
VRF1 {
port 900;
}
VRF2 {
port 901;
}
VRF3 {
port 902;
}
}
set interfaces lo0 unit 100 family inet address 100.100.1.1/32
set interfaces lo0 unit 200 family inet address 100.100.2.1/32
set interfaces lo0 unit 300 family inet address 100.100.3.1/32
set routing-instances VRF1 interface lo0.100
set routing-instances VRF2 interface lo0.200
set routing-instances VRF3 interface lo0.300
Results
root@PE1# run show services rpm twamp server
Connection Client Client Server Server Session Auth
ID address port address port count mode
29 30.2.1.1 53108 100.100.1.1 900 1 Unauthenticated
30 31.2.2.1 59718 100.100.3.1 902 1 Unauthenticated
28 31.2.3.1 39126 100.100.2.1 901 1 Unauthenticated
Session Connection Sender Sender Reflector Reflector Session Auth
ID ID address port address port state mode
13 29 30.2.1.1 43148 100.100.1.1 5000 Active Unauthenticated
14 30 31.2.2.1 41885 100.100.3.1 5000 Active Unauthenticated
12 28 31.2.3.1 45628 100.100.2.1 5000 Active Unauthenticated
Statistics and Debugging
Since these are hostbased PFE /inline using LU the statistics need to be checked in PFE.
From PFE
VMX-0(PE1 vty)# show jnh inline-twamp statistics
TWAMP Inline Server Data Statistics
Num Data Packets Twamped in Lu : 17816
TWAMP Inline Client Data Statistics
Num Data Packets Sent by Lu : 0
Num Data Packets Received by Lu : 0
Num Data Packets Sent by ukern : 0
Data Packets Tx bad len in ukern : 0
Data Packets Tx error in ukern : 0
From RE
root@PE1> show services rpm twamp client probe-results control-connection < >
root@PE1> show services rpm twamp client probe-results test-session < >
You can also use firewall filters
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-IN term 10 from protocol icmp
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-IN term 10 from protocol tcp
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-IN term 10 from protocol udp
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-IN term 10 then count COUNT-IN-TWAMP
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-IN term 10 then accept
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-IN term 20 then count TWAMP-OTHERS-IN
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-IN term 20 then accept
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-OUT term 10 from protocol icmp
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-OUT term 10 from protocol tcp
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-OUT term 10 from protocol udp
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-OUT term 10 then count COUNT-OUT-TWAMP
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-OUT term 10 then accept
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-OUT term 20 then count TWAMP-OTHERS-OUT
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-OUT term 20 then accept
set interfaces si-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet
set interfaces si-0/0/0 unit 10 rpm twamp-server
set interfaces si-0/0/0 unit 10 family inet filter input TWAMP-IN
set interfaces si-0/0/0 unit 10 family inet filter output TWAMP-OUT
set interfaces si-0/0/0 unit 10 family inet address 45.1.1.1/32
Issues with NAT
If TWAMP Full is used and there is a firewall natting the source/dest IP, note that the TWAMP full uses TCP initially in the control connection message. The TWAMP payload carries the original client IP. Along the way only the outer header is NAT’d and we not see it work as exepcted. This is because the payload carries the session information and that would not be NAT’d. For this, we need to enable ALG for TWAMP in the firewall to ensure it copies the payload information to the outer header.
Configure ALG on vSRX
set security alg twamp
Configure a custom application for TWAMP with destination port as 864(We can pick a different port as well) and attach the twamp ALG.
set applications application cust-twamp application-protocol twamp
set applications application cust-twamp protocol tcp
set applications application cust-twamp source-port 0-65535
set applications application cust-twamp destination-port 864
set applications application cust-twamp inactivity-timeout 1800
Configure two separate security policies, one for TCP control port with the above custom application and another policy to allow UDP traffic.
set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy default-permit match source-address any
set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy default-permit match destination-address any
set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy default-permit match application cust-twamp
set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy allow-udp match source-address any
set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy allow-udp match destination-address any
set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy allow-udp match application any
set security policies from-zone untrust to-zone trust policy allow-udp then permit
Another alternative is to use twamp-lite. This will ensure there is no control connection at all and just send the UDP probes. This will also by pass the NAT issue and it would work.
Firewall filters on si- interfaces
When filters are applied on si interfaces, only data traffic hits it. The TWAMP control packets hits the RE a filter has to be on the protect host.
Config
set firewall family inet filter PROTECTHOST term 10 from protocol tcp
set firewall family inet filter PROTECTHOST term 10 from destination-port 862
set firewall family inet filter PROTECTHOST term 10 then count TWAMP-CONTROL-LO0-filter
set firewall family inet filter PROTECTHOST term 10 then accept
set firewall family inet filter PROTECTHOST term accept-all then accept
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-NEW term 10 from protocol tcp
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-NEW term 10 from port 862
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-NEW term 10 then count COUNT-862-CONTROL
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-NEW term 10 then accept
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-NEW term 30 from port 5000
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-NEW term 30 then count TWAMP-SESSION
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-NEW term 30 then accept
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-NEW term 20 then count REMAINING-SESSION
set firewall family inet filter TWAMP-NEW term 20 then accept
Apply the above config on the si- interface and notice that only TWAMP session packets will be hit.
set interfaces si-0/0/0 unit 10 family inet filter input TWAMP-NEW
set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet filter input PROTECTHOST
Verify
Filter: TWAMP-NEW
Counters:
Name Bytes Packets
COUNT-862-CONTROL 0 0
REMAINING-SESSION 0 0
TWAMP-SESSION 614238 8902
Filter: PROTECTHOST
Counters:
Name Bytes Packets
TWAMP-CONTROL-LO0-filter 1024 13
linux junos mx